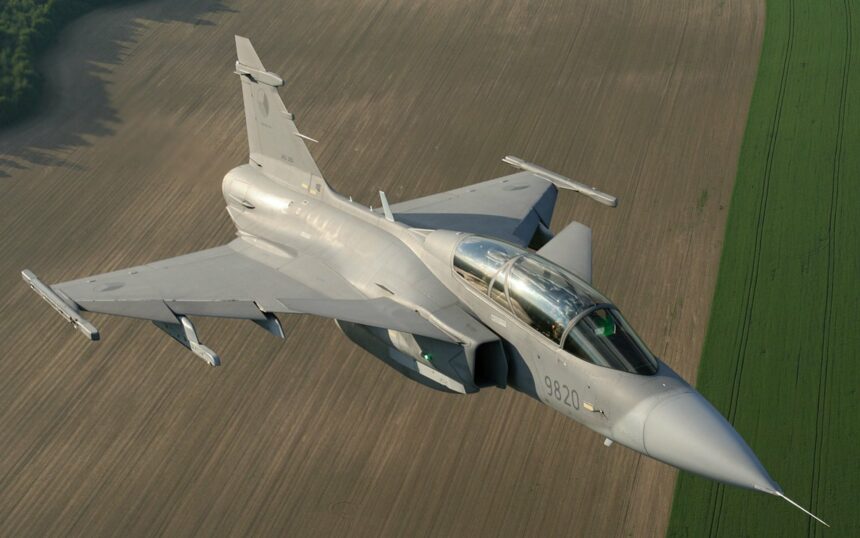
SAAB JAS 39 “Gripen”, a highly capable non-stealth jet fighter, took its maiden flight in December of 1988. Designed as a replacement for the ageing SAAB 35 “Viggen” and SAAB 37 “Draken,” it entered official service in 1997.
This aircraft resulted from a collaborative effort involving SAAB, SAAB Microwave Systems (formerly Ericsson), Volvo Aero Corporation, SAAB Avitronics, and FFV Aerotech. It marked Sweden’s inaugural venture into multirole combat aircraft, encompassing interception, ground-attack, and reconnaissance capabilities. As a fourth-generation fighter, the JAS 39 was equipped with cutting-edge digital controls and contemporary weapon systems.
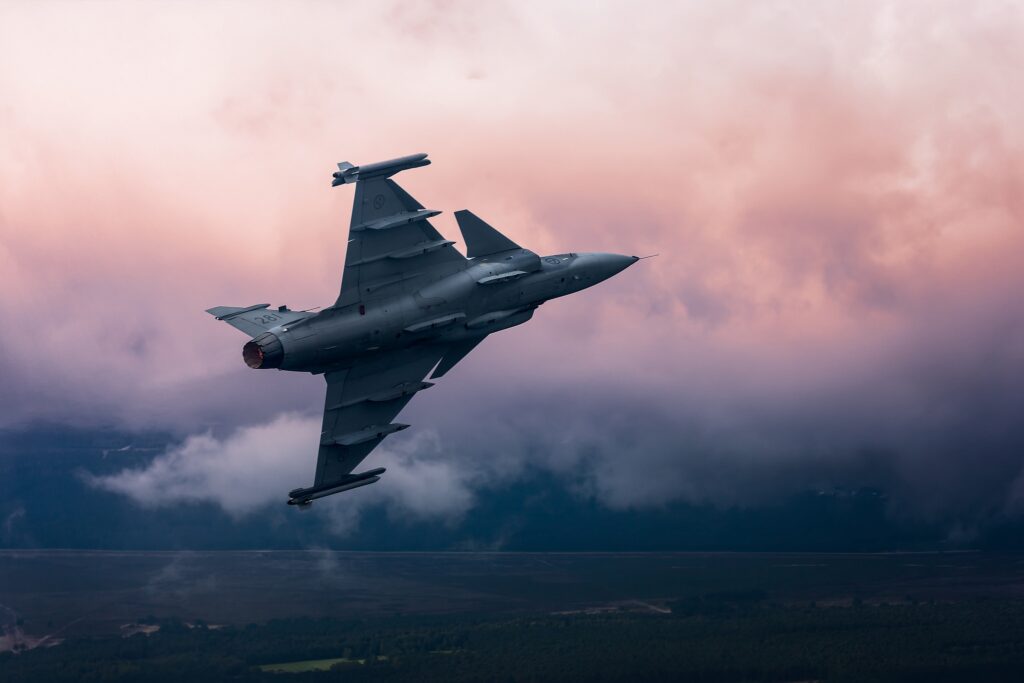

The origins of the “Griffon” trace back to the 1970s when the Swedish government acknowledged the need for a multirole fighter to maintain the relevance of the country’s Air Force. After briefly considering American F-16 and F18 fighters, Sweden opted to pursue its domestic design. SAAB was tasked with bringing this vision to life, resulting in the single-engine SAAB JAS 39 available in B and D variants, with extended canopies for two-man crews.
Since 1997, approximately 204 SAAB JAS 39s have been manufactured and delivered in multiple batches to the Swedish Air Force, with around 70 allocated domestically and the remainder serving in various international air forces, including Brazil, the Czech Republic, Hungary, South Africa, Thailand, and a few employed by the UK for training purposes.
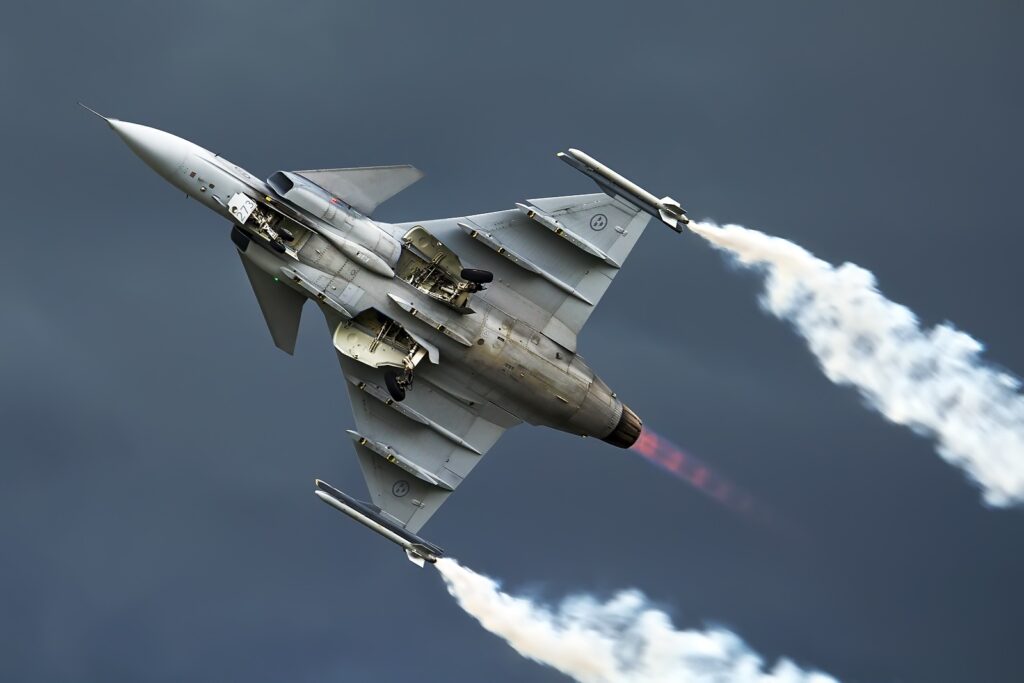

The “Gripen” is powered by a Volvo RM12 after-burning turbofan engine, capable of generating 54 kN (12,000 lbf) thrust in dry conditions or 80.5 kN (18,100 lbf) with afterburners engaged. This power plant propels the aircraft to a top speed of Mach 2 and offers an effective combat range of about 497 miles (800 km). The fighter can operate at altitudes of up to 9.47 miles (15.24 km) above sea level.
In terms of armament, the “Gripen” is armed with a 27 mm Mauser BK-27 revolver cannon equipped with 120 rounds (in the single-seat version). Additionally, it features eight weapons mounting points, two under the fuselage, two under each wing, and one on the wingtips. These mounting points provide flexibility for various armament options, including missiles and laser-guided bombs.
The E-version of the “Gripen” represents a significant upgrade, boasting a more powerful engine, extended range, enhanced ordnance-carrying capabilities, and the addition of new features such as an SA-radar, Infrared Search and Track System (IRST), advanced electronic warfare, and communication systems, ensuring that the “Gripen” remains a formidable contender among non-stealth fighter aircraft.