From new vaccines to the first drugs of their kind for hard-to-treat disorders, 2023 has been a year full of medical breakthroughs. They offer opportunities for people to protect themselves from diseases, slow down the effects on others, and even incorporate artificial intelligence into cancer diagnoses. Here are seven of the biggest innovations in the health and science space this year.
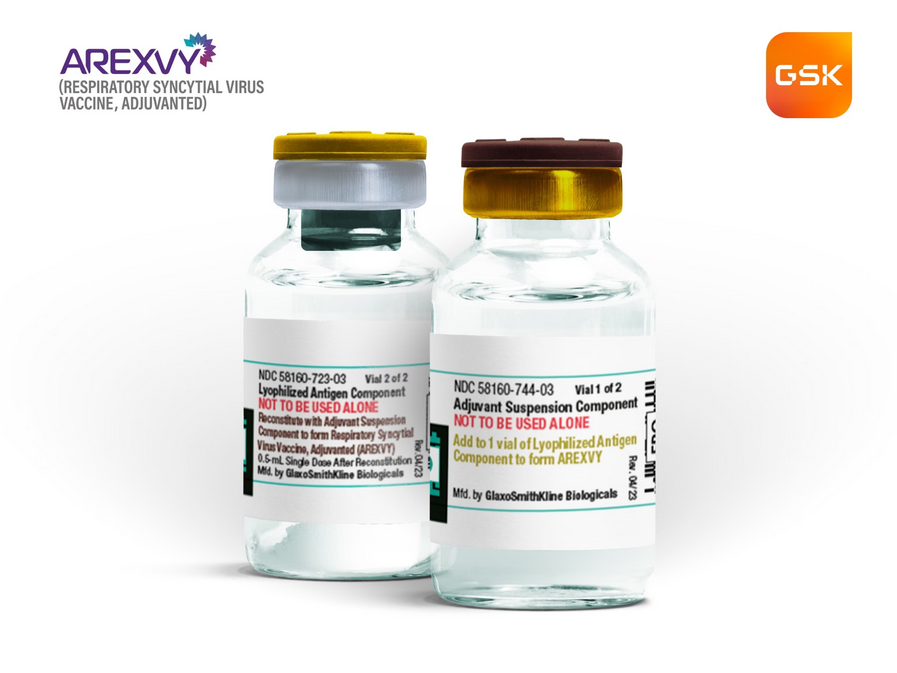
New RSV vaccines and immunizations
In 2023, a significant breakthrough emerged in the battle against Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV). The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted approval for multiple vaccines, marking a historic moment after years of setbacks. Notably, vaccines targeted different demographics, including adults over 60, pregnant mothers, and infants under 8 months old. These advancements offer a crucial means to protect vulnerable populations and address the substantial public health impact of RSV.
1st CRISPR gene-editing technique to treat sickle cell
The FDA’s approval of two gene therapies for treating sickle cell disease (SCD) in 2023, including the groundbreaking CRISPR gene-editing therapy, marks a pivotal moment in genetic medicine. These therapies, Lyfgenia and Casgevy, employ innovative approaches to address the challenges posed by SCD, aiming to provide patients with a milder form of the disease. This development offers hope for improved quality of life for individuals grappling with the multifaceted impacts of SCD.

Over-the-counter birth control pill
July 2023 witnessed a transformative step in reproductive health with the FDA’s approval of the first over-the-counter birth control pill, Opill. Manufactured by HRA Pharma and Perrigo, Opill is a progestin-only pill, enhancing accessibility and expanding contraceptive choices for millions in the United States. The move is expected to empower individuals, especially those facing barriers to prescription-based birth control, by making this crucial healthcare option readily available.

Scientists pinpoint possible cause of morning sickness
A breakthrough in understanding morning sickness was achieved in 2023 as researchers identified a link between the hormone GDF15, produced by the fetus, and severe nausea and vomiting during pregnancy. The discovery, published in the journal Nature, sheds light on the physiological basis of morning sickness. This newfound knowledge offers prospects for tailored treatments, potentially alleviating the suffering of pregnant individuals and addressing severe forms like hyperemesis gravidarum.
First drug fully approved by the FDA to treat Alzheimer’s
July 2023 marked a significant milestone in the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease with the FDA’s full approval of Leqembi. Developed by Eisai and Biogen, Leqembi is the first drug of its kind proven to slow cognitive decline in early-stage Alzheimer’s patients. While offering hope for individuals with the disease, questions linger about the drug’s accessibility. Its approval underlines the ongoing challenge of balancing innovation with ensuring widespread access to transformative treatments.

mRNA vaccine to treat pancreatic cancer
A promising development in cancer treatment emerged in 2023 with the development of a personalized mRNA vaccine against pancreatic cancer. Collaborative efforts, including funding from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and BioNTech’s expertise, led to early clinical trials showing encouraging results. The vaccine, administered alongside immune system-boosting drugs, demonstrated efficacy in triggering immune responses targeting cancer cells. While presenting hope for pancreatic cancer patients, further research is needed to refine and expand the application of this innovative approach.
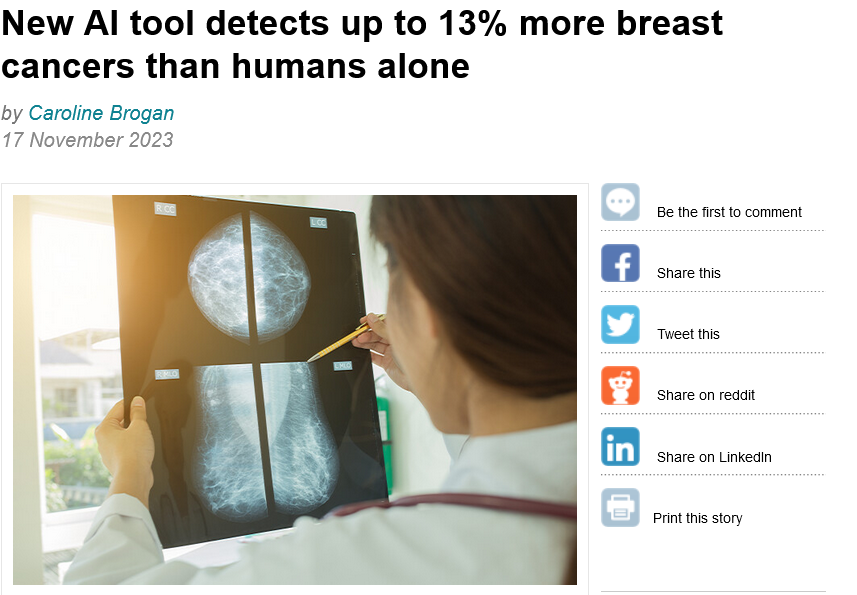
AI boosts breast cancer detection rates
Artificial Intelligence (AI) made significant strides in breast cancer detection in 2023 with the introduction of Mia, a tool developed by Imperial College London and Kheiron Medical Technologies. Mia demonstrated its efficacy by detecting 13% more early breast cancers compared to human screenings. This AI tool serves as a valuable complement to traditional screening methods, acting as a safety net to prevent missed cancer signs. The results highlight the potential of AI to enhance early detection and improve outcomes in breast cancer care.