A groundbreaking mission to the Moon is underway, as a suite of NASA science instruments and technology demonstrations journey to our celestial neighbor. These payloads, launched aboard Intuitive Machines’ Nova-C lander, aim to provide crucial insights into the lunar surface environment and test technologies essential for future lunar exploration.
Led by NASA’s CLPS initiative and Artemis campaign, these deliveries mark a significant step towards humanity’s return to the Moon after more than half a century. With scientific instruments onboard, this mission will not only conduct groundbreaking research but also support the growth of the commercial space economy, showcasing American technology and innovation.
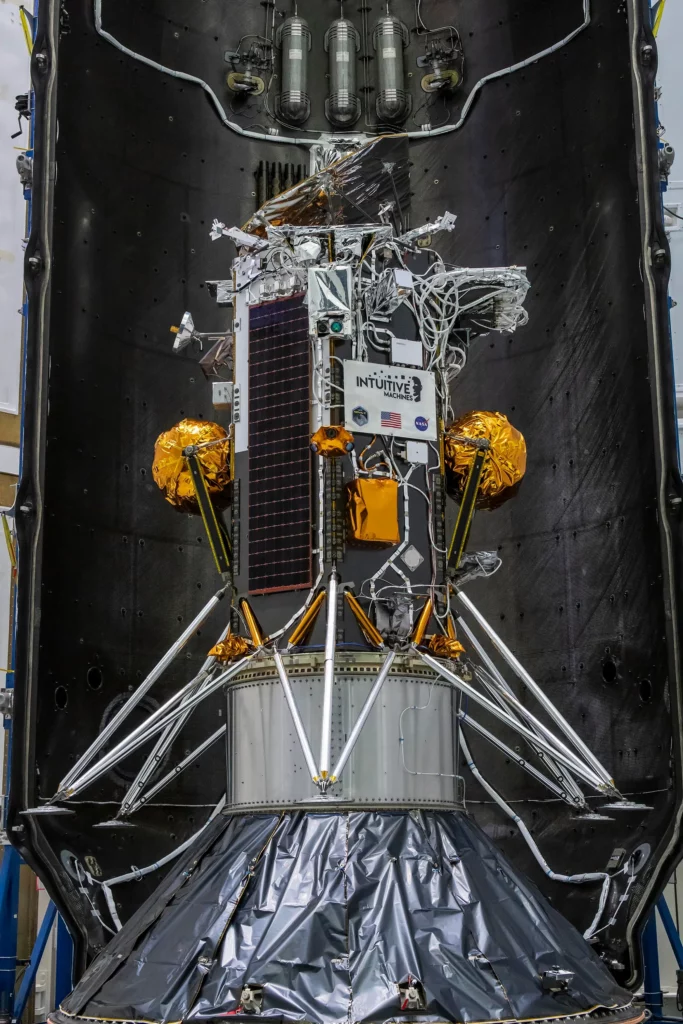

The payloads onboard include instruments to measure cryogenic engine fuel usage, study plume-surface interactions during descent, and test precision landing technologies. Once on the lunar surface, these instruments will focus on investigating space weather, lunar surface interactions, and radio astronomy. Additionally, the lander will deploy retroreflectors to aid in communication and navigation for future missions.
Key NASA science payloads include:
- Lunar Node 1 Navigation Demonstrator: A CubeSat-sized experiment demonstrating autonomous navigation for future missions.
- Laser Retroreflector Array: Eight retroreflectors enabling precision laser ranging.
- Navigation Doppler Lidar: A guidance system for descent and landing, measuring speed, direction, and altitude with high precision.
- Radio Frequency Mass Gauge: A technology demonstration measuring propellant levels in spacecraft tanks.
- Radio-wave Observations at the Lunar Surface: Observing the Moon’s surface environment in radio frequencies.
- Stereo Cameras for Lunar Plume-Surface Studies: Capturing imagery of surface changes during and after descent.
Scheduled to land near the Moon’s South Pole region, this mission will provide valuable scientific data about Earth’s nearest neighbour. Landing near Malapert A, the lander will help mission planners understand communication challenges from locations with Earth low on the lunar horizon. This mission sets the stage for future Artemis missions, paving the way for the first woman and person of colour to explore the Moon.