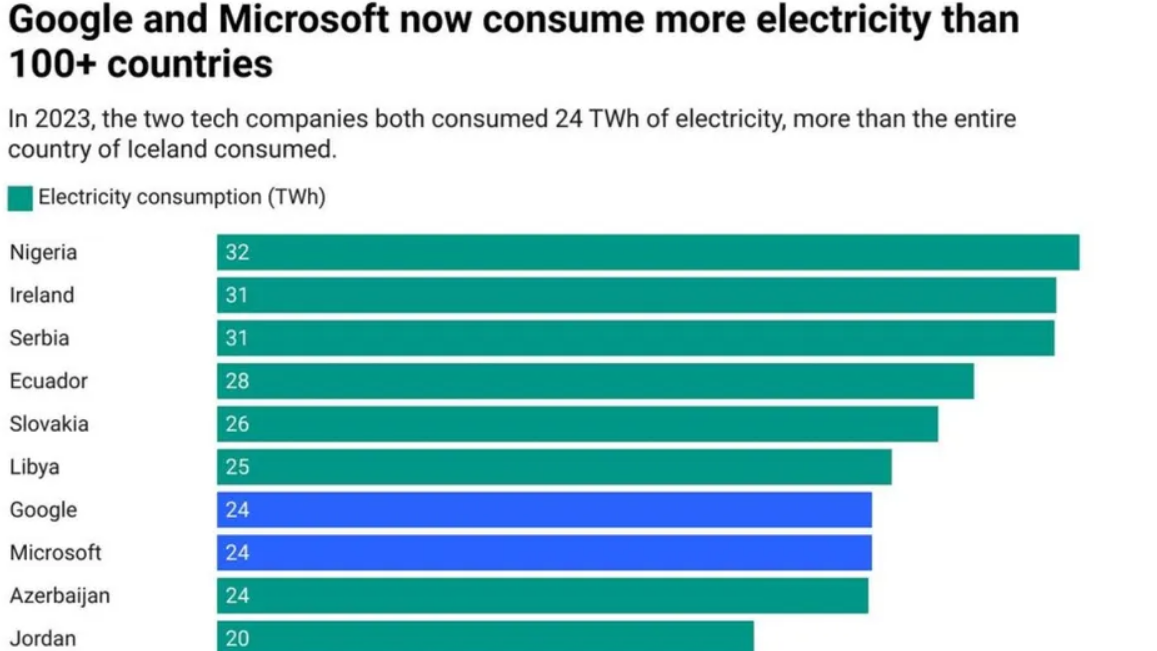
In 2023, Google and Microsoft each consumed a staggering 24 TWh of electricity, underscoring the massive energy demands of today’s tech giants. These companies, both at the forefront of technological advancements, are leading the charge in adopting renewable energy as a viable power source for their sophisticated operations. Their data centres, which keep cloud services and AI efforts running, are major energy consumers.
Generative AI has revolutionized various sectors including medicine, education, music, and computing. Beyond AI-powered chatbots and image-generation tools, the landscape is becoming increasingly advanced and demanding. This evolution comes with significant energy requirements, both in terms of electricity and water — with cooling needs amounting to roughly one water bottle per query.
In 2023, the combined electricity consumption of Microsoft and Google reached 48 TWh (24 TWh each). According to an analysis by Michael Thomas, this consumption surpasses that of over 100 nations, including Ghana and Tunisia.
Despite the environmental impact, both Google and Microsoft are actively promoting renewable energy and seeking alternative power sources. Their electricity usage is comparable to that of Azerbaijan, which has a population of 10.14 million and a GDP of $78.7 billion.
AI is proving to be a lucrative field. Microsoft recently became the world’s most valuable company, with a market valuation exceeding $3 trillion. Analysts attribute this success to Microsoft’s early investment in AI. CEO Satya Nadella highlighted the company’s increased revenue, operating income, and net income as being driven by the “new era of AI transformation.”
Both Microsoft and Google maintain extensive data centres for cloud services, which consume substantial power and water for cooling. As their involvement in AI deepens, power consumption has likely increased.
Elon Musk has expressed concerns about the exponential growth of AI outpacing power availability by 2025. In line with these concerns, Sam Altman of OpenAI is exploring alternative power sources, with nuclear fusion being a top contender. Microsoft has partnered with Helion, aiming to generate nuclear energy through fusion by 2028. Helion is also training LLMs to expedite the regulatory process.
While nuclear fusion offers an environmentally friendly solution for AI’s power needs, scientists argue it may be “too late to address the climate crisis.” They advocate for fission and renewable energy as more immediate and practical options.
In summary, as AI continues to advance and expand, its energy demands will remain a critical challenge. The efforts of tech giants like Google and Microsoft in pursuing renewable and alternative energy sources will be crucial in balancing technological progress with environmental sustainability.